#30DayProjectChallenge Day 6: To-Do App with Local Storage
By TechInfoWithAshish - 9-12-2023
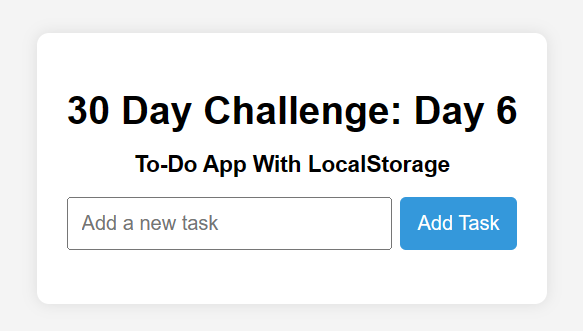
Hello everyone! Welcome to Day 6 of the #30DayProjectChallenge. Today, we're enhancing our To-Do app with Local Storage using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. This is a crucial step in building web applications that remember user data across sessions, making them truly functional and user-friendly.
Understanding Data Persistence with Local Storage
In the previous blog, we created a basic To-Do list application that allowed users to add and delete tasks. However, when the page was refreshed, all tasks were lost. Building upon that foundation, today's focus is on implementing Local Storage to persist our tasks, ensuring they remain available even after the browser is closed and reopened.
What You'll Learn in This Tutorial
- Local Storage API: Master the browser's localStorage API for client-side data storage
- Data Persistence: Understand how to save and retrieve data that persists across browser sessions
- JSON Serialization: Learn how to convert JavaScript objects and arrays to JSON strings for storage
- Data Synchronization: Understand how to keep the UI and storage in sync
- State Management: Learn how to manage application state and restore it on page load
- Error Handling: Implement error handling for storage operations and quota limits
- Storage Best Practices: Learn when and how to use localStorage effectively
Key Features of Our To-Do App with Local Storage
Here are the key features of our enhanced To-Do app with Local Storage:
- Task Input Field: Users can enter their tasks in a user-friendly input field with validation
- Add Task Button: On clicking this button, the task gets added to the task list and automatically saved in Local Storage
- Persistent Storage: All tasks are saved to the browser's Local Storage, ensuring they persist across sessions
- Automatic Restoration: Tasks are automatically loaded from Local Storage when the page loads
Advanced Features We've Implemented
Additionally, we've introduced comprehensive features that enhance functionality:
- Input Validation: Prevents adding empty tasks with clear error messages that guide users
- Task List Management: Dynamically generated task list that displays all saved tasks
- Delete Functionality: Each task has a delete button that removes it from both the display and Local Storage
- Real-Time Synchronization: Every change (add/delete) is immediately saved to Local Storage
- Data Restoration: On page load, all tasks are automatically retrieved from Local Storage and displayed
- Error Handling: Comprehensive error handling for storage operations, including quota exceeded errors
Why Local Storage is Essential
Local Storage is a powerful browser API that enables web applications to store data locally on the user's device. Unlike session storage, localStorage data persists even after the browser is closed, making it perfect for applications like to-do lists, notes, and user preferences. Key benefits include:
- Data Persistence: Tasks remain available even after closing the browser
- Offline Functionality: Applications can work offline without server connectivity
- Improved User Experience: Users don't lose their data when refreshing the page
- Client-Side Storage: Data is stored locally, reducing server load and improving performance
- Privacy: Data stays on the user's device, enhancing privacy and security
Understanding the Local Storage API
The Local Storage API provides simple methods for storing and retrieving data:
- localStorage.setItem(key, value): Saves data to localStorage with a specified key
- localStorage.getItem(key): Retrieves data from localStorage using the key
- localStorage.removeItem(key): Removes a specific item from localStorage
- localStorage.clear(): Clears all data from localStorage
- localStorage.key(index): Retrieves the key at a specific index
- localStorage.length: Returns the number of items stored in localStorage
Working with JSON in Local Storage
Since localStorage can only store strings, we need to convert JavaScript objects and arrays to JSON:
- JSON.stringify(): Converts JavaScript objects/arrays to JSON strings for storage
- JSON.parse(): Converts JSON strings back to JavaScript objects/arrays
- Error Handling: Handling parsing errors when retrieving corrupted or invalid data
- Data Validation: Validating data structure after retrieval from localStorage
Implementation Strategy
Our implementation follows a systematic approach:
- Save on Change: Every time a task is added or deleted, we immediately update localStorage
- Load on Init: When the page loads, we retrieve all tasks from localStorage and display them
- Data Structure: We store tasks as a JSON array for easy manipulation
- Synchronization: We ensure the UI and storage are always in sync
- Error Recovery: We handle cases where localStorage might be unavailable or corrupted
Best Practices for Local Storage
When working with Local Storage, follow these best practices:
- Always use try-catch blocks when working with localStorage to handle potential errors
- Check if localStorage is available before using it (some browsers or private modes may disable it)
- Be mindful of storage limits (typically 5-10MB per domain)
- Use meaningful keys that are easy to identify and maintain
- Validate data after retrieval to ensure it's in the expected format
- Don't store sensitive information like passwords or credit card numbers in localStorage
- Clean up old or unused data to prevent storage quota issues
- Consider using indexedDB for larger amounts of structured data
Storage Limitations and Considerations
It's important to understand localStorage limitations:
- Storage Quota: Most browsers limit localStorage to 5-10MB per domain
- Domain-Specific: Data is isolated to the specific domain and protocol
- Synchronous API: localStorage operations are synchronous and can block the main thread
- String Storage Only: All data must be converted to strings before storage
- No Expiration: Data persists indefinitely unless explicitly removed
- Privacy Modes: Some browsers may clear localStorage in private/incognito mode
Error Handling Strategies
Implementing robust error handling is crucial:
- Handle QuotaExceededError when storage limits are reached
- Check for localStorage availability before using it
- Validate JSON data after parsing to prevent runtime errors
- Provide fallback options when localStorage is unavailable
- Inform users when storage operations fail
- Implement data migration strategies for version updates
Real-World Applications
Local Storage is used in many real-world applications:
- To-do lists and task management apps
- User preferences and settings
- Shopping cart data in e-commerce sites
- Draft content in text editors and forms
- Game progress and high scores
- Offline data caching
- Theme and customization settings
Extending the Application
Once you've mastered localStorage basics, consider adding:
- Task editing functionality with persistent updates
- Task categories and filtering with saved preferences
- Due dates and reminders stored locally
- Task completion status tracking
- Export/import functionality for backing up tasks
- Data compression for storing more tasks
- Version control for data migration
With Local Storage integration, our To-Do app becomes a truly functional application that remembers user data across sessions. This enhancement significantly improves the user experience and demonstrates the power of client-side data persistence. As we continue our coding challenge, each enhancement builds upon previous knowledge, creating more sophisticated and useful applications. Tomorrow's challenge will add editing capabilities. Stay tuned for another exciting project. Happy coding!